Downloads
ACE Inhibitors-Induced Skin Reaction: A Case Report
Authors
Abstract
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are widely used as antihypertensives, remodeling agents in heart failure, to stop the progression of diabetic nephropathy, as well as for a variety of other clinical purposes. Some side effects of ACE inhibitors are well recognized such as dry cough, hypotension, hyperkaliemia, proteinuria, renal failure. Also, these substances are known to have a wide range of dermatological side effects in addition to their adverse effects on other systems. (1,2)
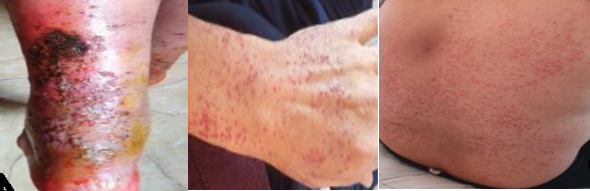
We report the case of a 46-year-old man treated for dilated cardiomyopathy with severe left ventricle dysfunction, who developed a cutaneous reaction secondary to the introduction of an ACE inhibitor.
Article Details
Published
2023-08-15
Issue
Section
Articles
How to Cite
ACE Inhibitors-Induced Skin Reaction: A Case Report. (2023). Research and Analysis Journal, 6(8), 01-03. https://doi.org/10.18535/raj.v6i8.416



