Study the Prevalence of Depression in Patients Attending Comprehensive Care Centre, Islamabad, Pakistan
Authors
Abstract
Abstract:
Depression is one of the most common neuropsychiatric complications of HIV disease, and this leads to worse HIV-related health outcomes. With 350 million people affected worldwide, rates of depression are roughly two times greater in people living with HIV than in the general population.
Objective: Determine prevalence of depression in patients attending Comprehensive Care Centre Shifa international Hospital, Islamabad
Design: Descriptive cross-sectional quantitative study.
Settings: Shifa international Hospital, Islamabad Comprehensive Care Centre,
Methods: This data is from a bigger study ‘prevalence of alcohol use disorders and depression in patients attending Comprehensive Care Centre (CCC). The study population consisted of PLWHA attending the CCC. Two hundred and seventy-two (N=272) participants from CCC attendants were recruited. All consenting male and female aged 18-65 years were interviewed using the researcher’s designed questioner to collect their socio-demographic characteristics. Fully completed questionnaires were entered into excel sheets and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Version 20.
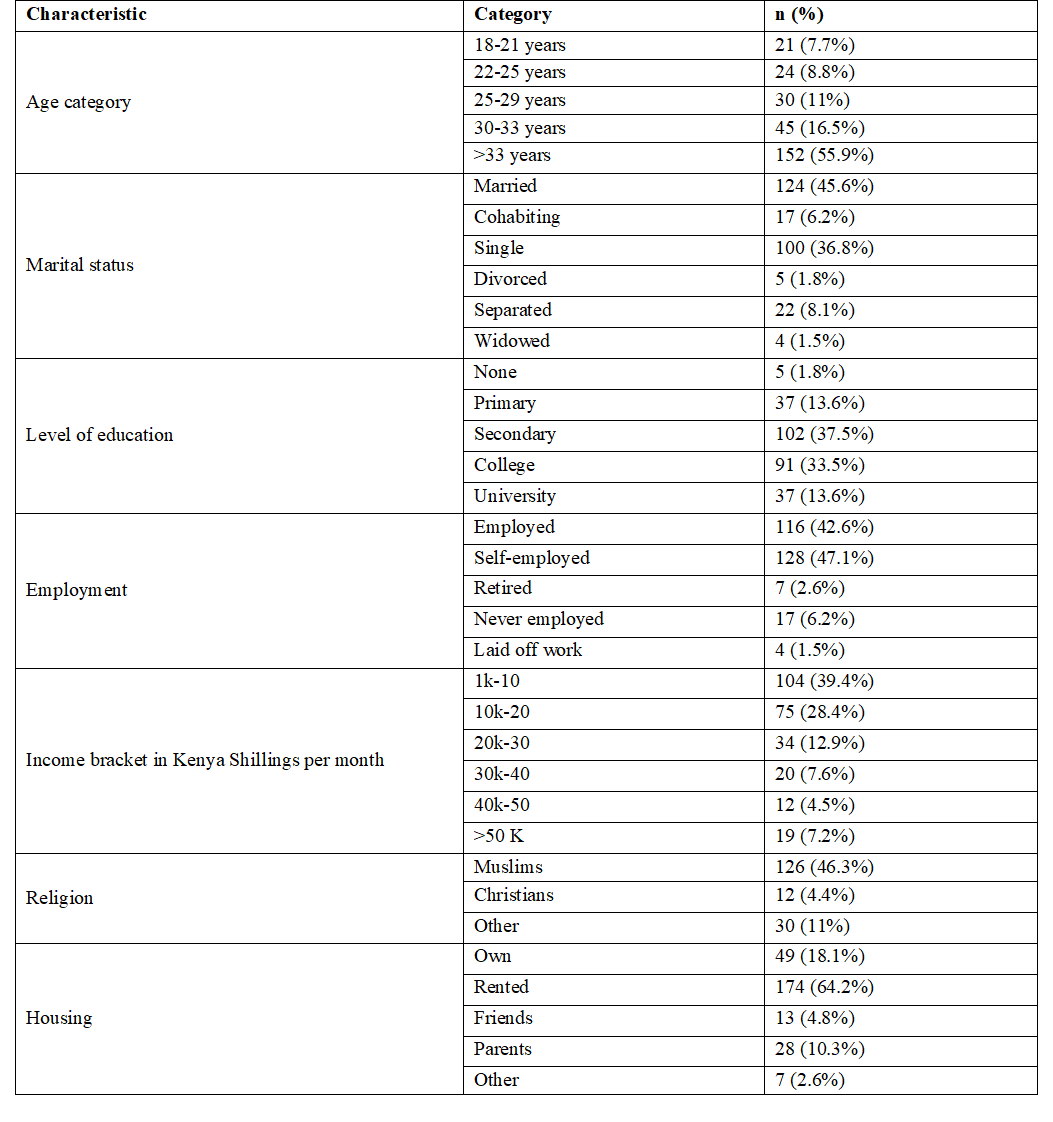
Results: The overall prevalence of depression was 23.8%, with mild depression at 9.7%, moderate depression at 10.4% and severe depression accounting for 3.7%, respectively. Depression was associated with alcohol use (p=0.024). A significant difference between depression and age where depression levels worsens as age advances; respondents in age category of 18-21 years had less or no depression compared to those in the age category of 33 years and above. We found an association between depression and employment. Those laid-off work (1/3), and the retired (15%) had more depression compared to the employed (11%) or self-employed 6%, with a P value of 0.55 (borderline). On multivariate analysis severity of depression (OR=5.5, 95% CI of OR [2.1 –14.3], p<0.0001) was associated with male gender (OR=10, 95% CI of OR [3.6 –28.3], p<0.0001).
Conclusion: The study findings indicate a high prevalence of depressive symptoms in patients attending the CCC. There is need to set-up appropriate interventions and strategies to reduce the prevalence of mental health disorders into routine HIV clinical care and support.