Vol. 7 No. 12 (2024)
Published:
2024-12-03
Articles
-
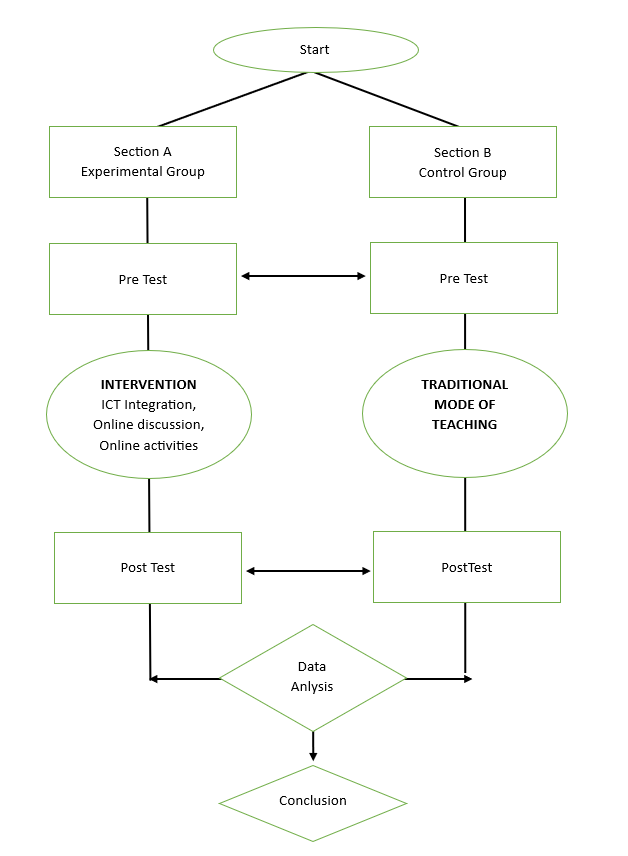
Students’ Evaluation of The Academic Performance Through Interactive Multimedia Integration in A State College
01-05 331 175 -
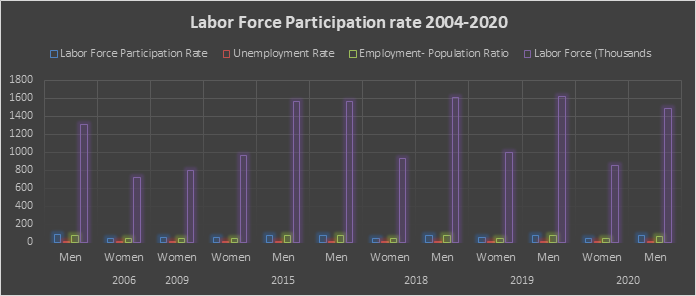
Five to Five: Sex-Disaggregated Issues in Bicol Region (V), Philippines Through the Lens of SDG 5 None
06-22 719 274 -
-
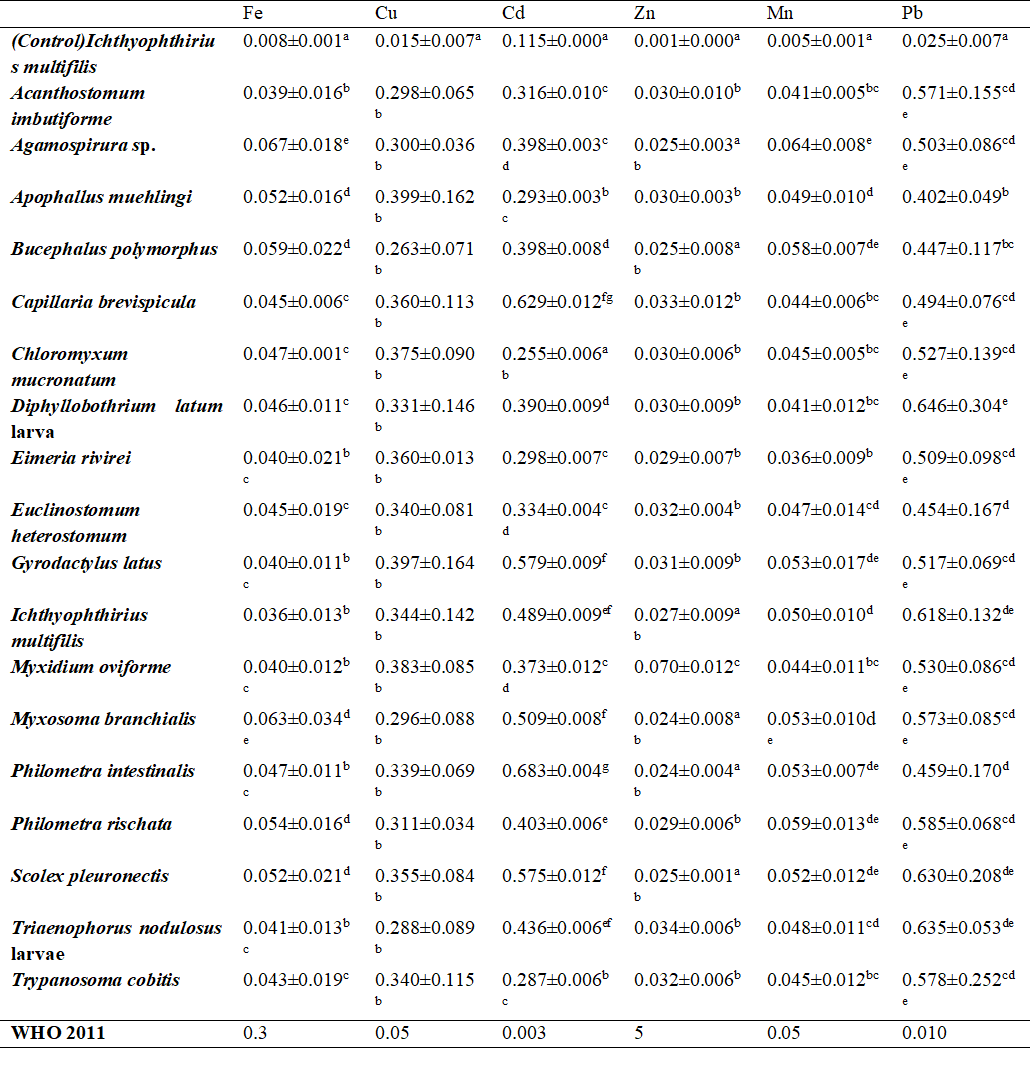
Clarias Gariepinus Parasites as Bioindicator For Assessing Water Quality in Omi Dam, Kogi State, Nigeria
29-35 187 77 -
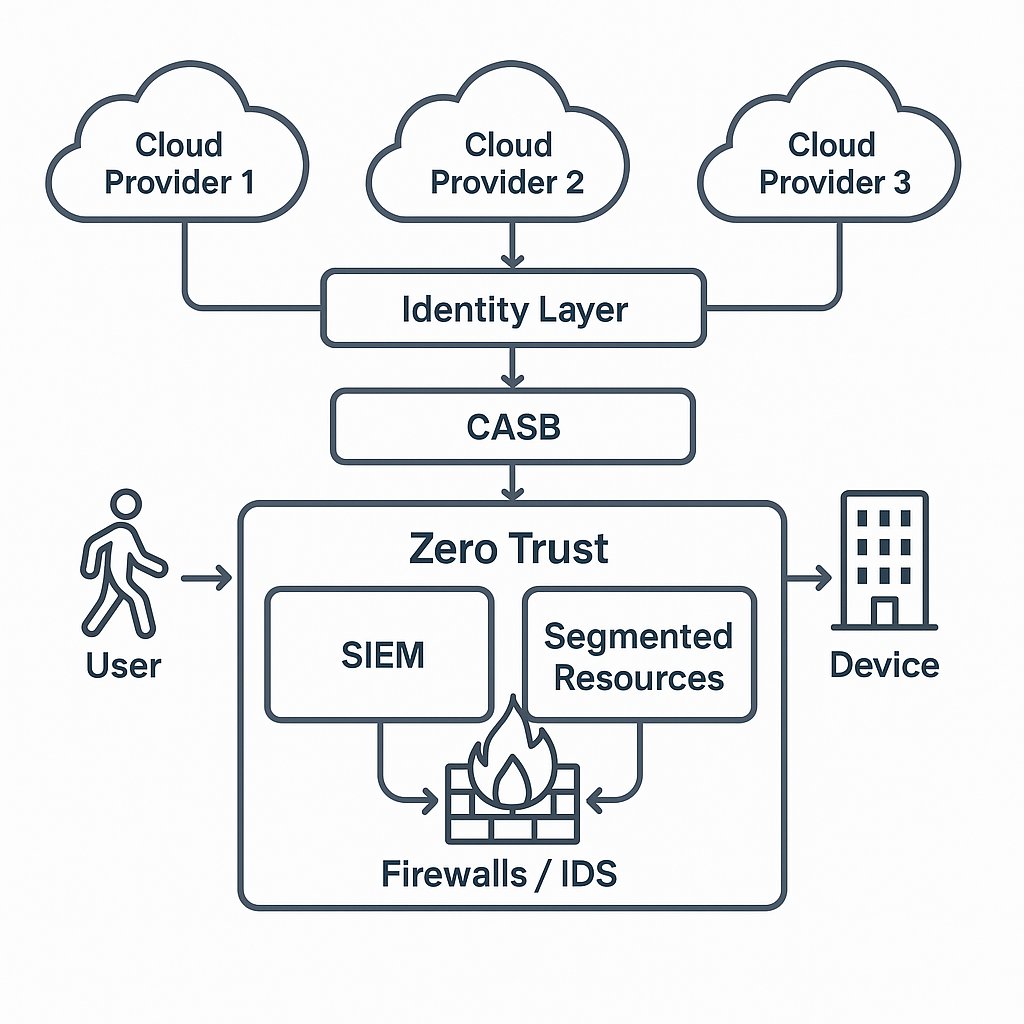
Zero Trust in Practice: How Enterprises Are Implementing Zero Trust Architectures Across Multi-Cloud System
36-46 277 74