Downloads
Brain Targeted Drug Delivery System: A Review
Authors
Abstract
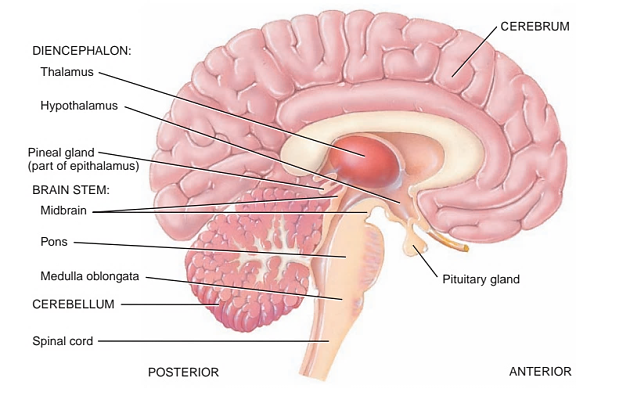
Brain is the most sophisticated and important organ of our body. Together with spinal cord it control all actions, all functions voluntary or involuntary and plays a vital role in managing various organ systems of our body. It has its own protective barriers that protects the brain from various pathogens and toxins that may cause the harm. These barriers are namely Blood-Brain barrier and Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier. The highly lipophilic nature of these barriers helps them in protecting the brain, allowing the passage of only highly lipophilic drugs to the brain through blood. However when there is an infection or injury in brain, the same barriers pose a hindrance in the delivery of drugs to the brain for treatment. Usually, drugs are usually hydrophilic in nature and since barriers of brain are lipophilic in nature, the finds it hard to cross these barriers and reach the brain. In order to overcome the problem in drug delivery to the brain as a target organ various drug delivery techniques were developed. Invasive and non-invasive approaches are two main approaches that are used to deliver drug to brain. In invasive approach the permeability of BBB is decreased or the drug is directly administered, whereas in non-invasive approach the drug molecule is altered to enhance its lipophilicity allowing its passage to the brain. This review aims to describe the various brain targeted drug delivery system..



